#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# # 1. Introduction
#  #
# - HTML version of textbook: [http://openbookproject.net/thinkcs/python/english3e/way_of_the_program.html](http://openbookproject.net/thinkcs/python/english3e/way_of_the_program.html)
# - PDF version of textbook: [http://www.greenteapress.com/thinkpython/thinkCSpy/thinkCSpy.pdf](http://www.greenteapress.com/thinkpython/thinkCSpy/thinkCSpy.pdf)
#
# ## Topics:
# - Python and its features
# - Ways to run Python code
# - Computer program and its building blocks
# - Errors and Debugging
#
# ## 1.1 Python Programming Language
#
# - the single most important skill for a computer scientist is problem solving
# - Python is a tool that helps computer scientists and programmers solve problems by writing code
# - One of the most popular programming languages used in various fields: Data Science and Machine Learning, Security, Web Apps, etc.
# - Popularity has been increasing over the years: https://www.tiobe.com/tiobe-index/
# ## 1.2 Python Features
# - high-level general purpose programming language such as PHP, Perl, Java, JavaScript, C++, etc.
# - as opposed to low level machine language such as assembly
# - interpreted language; needs Python interpreter to execute Python code
# - platform independent/portable; python programs can be run in many platforms including Raspberry Pi
# - open source, can be freely downloaded and use: http://python.org
# - installed using Python package manager such as Anaconda or Miniconda: https://www.anaconda.com/download/
# - two versions Python 2.x and Python 3.x - Notebooks and the text use version 3.x which is the new standard
# ## 1.3 Zen of Python
# In[3]:
import this
# ## 1.4 Learning and Writing Python Code
# - one must write code to learn it
# - Python provides Chevron prompt to practice and use Python for quick calculations such as a calculator
# - most use code editors to write long program also called scripts
# - use [pythontutor.com](http://www.pythontutor.com/) to visualize code execution
#
# ### Chevron Prompt
# - Python provides a prompt in terminal - interactive mode
# - Once Python is installed and configured correctly, open terminal and type Python
# - [python.org](https://www.python.org/) also provides online Python prompt
# - \>>> You'll see this chevron/python prompt
# - \>>> 10 + 20.5
# - \>>> print('Hello World!')
#
# ### Jupyter Notebook
# - interactive notebook that can have live code, execution results and HTML, texts and multimedia contents!
# - great way to learn, experiment, and take notes while coding
# - Jupyter supports many programming languages such as C, C++, Java, JavaScript, etc.; Python is default!
#
# ### Python Script
# - using Intergrated Development Environment (IDE) such as PyScripter, PyCharm, and Visual Studio Code, Nodepad++, etc.
# - open VS Code or your favourite editor
# - create a hello.py file
# - type print('hello world!') and save the file
# - run the program from integreted terminal:
# ```bash
# python hello.py
# ```
# - run the program using GUI Run button
#
# ## 1.5 Computer Program
# - sequence of instructions that specifies how to perform a computation
# - some basic/fundamental concepts that make up a compupter program:
# - input, output, math, conditional execution and repition
#
#
# - HTML version of textbook: [http://openbookproject.net/thinkcs/python/english3e/way_of_the_program.html](http://openbookproject.net/thinkcs/python/english3e/way_of_the_program.html)
# - PDF version of textbook: [http://www.greenteapress.com/thinkpython/thinkCSpy/thinkCSpy.pdf](http://www.greenteapress.com/thinkpython/thinkCSpy/thinkCSpy.pdf)
#
# ## Topics:
# - Python and its features
# - Ways to run Python code
# - Computer program and its building blocks
# - Errors and Debugging
#
# ## 1.1 Python Programming Language
#
# - the single most important skill for a computer scientist is problem solving
# - Python is a tool that helps computer scientists and programmers solve problems by writing code
# - One of the most popular programming languages used in various fields: Data Science and Machine Learning, Security, Web Apps, etc.
# - Popularity has been increasing over the years: https://www.tiobe.com/tiobe-index/
# ## 1.2 Python Features
# - high-level general purpose programming language such as PHP, Perl, Java, JavaScript, C++, etc.
# - as opposed to low level machine language such as assembly
# - interpreted language; needs Python interpreter to execute Python code
# - platform independent/portable; python programs can be run in many platforms including Raspberry Pi
# - open source, can be freely downloaded and use: http://python.org
# - installed using Python package manager such as Anaconda or Miniconda: https://www.anaconda.com/download/
# - two versions Python 2.x and Python 3.x - Notebooks and the text use version 3.x which is the new standard
# ## 1.3 Zen of Python
# In[3]:
import this
# ## 1.4 Learning and Writing Python Code
# - one must write code to learn it
# - Python provides Chevron prompt to practice and use Python for quick calculations such as a calculator
# - most use code editors to write long program also called scripts
# - use [pythontutor.com](http://www.pythontutor.com/) to visualize code execution
#
# ### Chevron Prompt
# - Python provides a prompt in terminal - interactive mode
# - Once Python is installed and configured correctly, open terminal and type Python
# - [python.org](https://www.python.org/) also provides online Python prompt
# - \>>> You'll see this chevron/python prompt
# - \>>> 10 + 20.5
# - \>>> print('Hello World!')
#
# ### Jupyter Notebook
# - interactive notebook that can have live code, execution results and HTML, texts and multimedia contents!
# - great way to learn, experiment, and take notes while coding
# - Jupyter supports many programming languages such as C, C++, Java, JavaScript, etc.; Python is default!
#
# ### Python Script
# - using Intergrated Development Environment (IDE) such as PyScripter, PyCharm, and Visual Studio Code, Nodepad++, etc.
# - open VS Code or your favourite editor
# - create a hello.py file
# - type print('hello world!') and save the file
# - run the program from integreted terminal:
# ```bash
# python hello.py
# ```
# - run the program using GUI Run button
#
# ## 1.5 Computer Program
# - sequence of instructions that specifies how to perform a computation
# - some basic/fundamental concepts that make up a compupter program:
# - input, output, math, conditional execution and repition
# 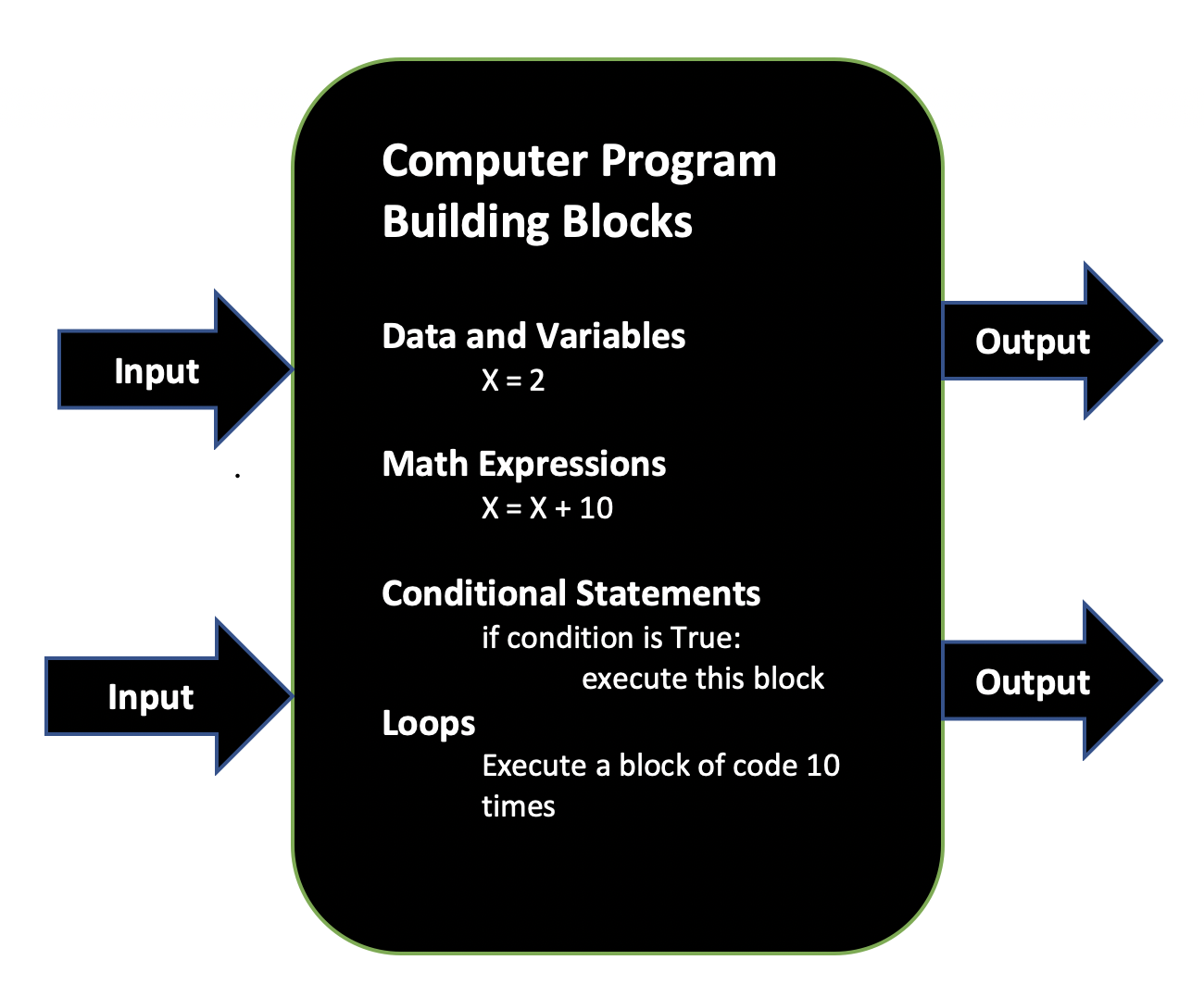 #
# ### input
# - get data from keyboard, a file, or some device
#
# ### output
# - display data/answer on screen, or save it to file or to a device
#
# ### math
# - basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
#
# ### conditional execution
# - check for certain condititions and execute appropriate sequence of statements
#
# ### repitition
# - perform some action repeatedly, usually with some variation every time
# ## 1.6 Debugging
# - finding and getting rid of bugs/errors
# - as long as humans write computer codes, there'll be always errors in computer program
# - although frustrating at times, it is one of the most intellectually rich, challenging, and interesting part of programming
# ## 1.7 Coding Errors
# - errors are also called bugs
# - 3 types: syntax, run-time and semantic
#
# ### Syntax errors
# - program needs to follow Python syntax or grammar; otherwise Python interpreter will not understand and tell programmers about the errors
# ### Run-time errors
# - also called run-time exceptions
# - errors appear while programming is running
# - can be handled to certain extent
#
# ### Semantic errors
# - program runs fine but gives wrong answer
# - can be identified and removed by doing plenty of testing
# ## 1.8 The First Program
# - python programs are usually called scripts
# In[2]:
#----------------------------------------------------------
# hello world program
# by: John Doe
# Jan 1 2017
# Copyright: Anyone may freely copy or modify this program
#----------------------------------------------------------
print('hello world!') # say hello to the beautiful world!
# ## 1.9 Exercises
#
# ### 1. Write a hello world script
# - write a python script that prints "Hello World!" as an output on the console
#
# ### 2. Solve kattis hello problem
# - create an account in Kattis: https://open.kattis.com/login
# - login and solve the hello problem: https://open.kattis.com/problems/hello
#
# ### 3. ASCII Art
# - learn about ASCII Art
# - print some ASCII Arts, texts and pictures of your choice
# - use ASCII Art generator: http://patorjk.com/software/taag/#p=display&f=Graffiti&t=Type%20Something%20
#
# ### 4. Write a script that prints various stages of hangman game
# - game description: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hangman_(game)
# - produce the output seen in Example game section of the Wikipedia page
#
# In[ ]:
#
# ### input
# - get data from keyboard, a file, or some device
#
# ### output
# - display data/answer on screen, or save it to file or to a device
#
# ### math
# - basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
#
# ### conditional execution
# - check for certain condititions and execute appropriate sequence of statements
#
# ### repitition
# - perform some action repeatedly, usually with some variation every time
# ## 1.6 Debugging
# - finding and getting rid of bugs/errors
# - as long as humans write computer codes, there'll be always errors in computer program
# - although frustrating at times, it is one of the most intellectually rich, challenging, and interesting part of programming
# ## 1.7 Coding Errors
# - errors are also called bugs
# - 3 types: syntax, run-time and semantic
#
# ### Syntax errors
# - program needs to follow Python syntax or grammar; otherwise Python interpreter will not understand and tell programmers about the errors
# ### Run-time errors
# - also called run-time exceptions
# - errors appear while programming is running
# - can be handled to certain extent
#
# ### Semantic errors
# - program runs fine but gives wrong answer
# - can be identified and removed by doing plenty of testing
# ## 1.8 The First Program
# - python programs are usually called scripts
# In[2]:
#----------------------------------------------------------
# hello world program
# by: John Doe
# Jan 1 2017
# Copyright: Anyone may freely copy or modify this program
#----------------------------------------------------------
print('hello world!') # say hello to the beautiful world!
# ## 1.9 Exercises
#
# ### 1. Write a hello world script
# - write a python script that prints "Hello World!" as an output on the console
#
# ### 2. Solve kattis hello problem
# - create an account in Kattis: https://open.kattis.com/login
# - login and solve the hello problem: https://open.kattis.com/problems/hello
#
# ### 3. ASCII Art
# - learn about ASCII Art
# - print some ASCII Arts, texts and pictures of your choice
# - use ASCII Art generator: http://patorjk.com/software/taag/#p=display&f=Graffiti&t=Type%20Something%20
#
# ### 4. Write a script that prints various stages of hangman game
# - game description: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hangman_(game)
# - produce the output seen in Example game section of the Wikipedia page
#
# In[ ]:
 #
# ### input
# - get data from keyboard, a file, or some device
#
# ### output
# - display data/answer on screen, or save it to file or to a device
#
# ### math
# - basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
#
# ### conditional execution
# - check for certain condititions and execute appropriate sequence of statements
#
# ### repitition
# - perform some action repeatedly, usually with some variation every time
# ## 1.6 Debugging
# - finding and getting rid of bugs/errors
# - as long as humans write computer codes, there'll be always errors in computer program
# - although frustrating at times, it is one of the most intellectually rich, challenging, and interesting part of programming
# ## 1.7 Coding Errors
# - errors are also called bugs
# - 3 types: syntax, run-time and semantic
#
# ### Syntax errors
# - program needs to follow Python syntax or grammar; otherwise Python interpreter will not understand and tell programmers about the errors
# ### Run-time errors
# - also called run-time exceptions
# - errors appear while programming is running
# - can be handled to certain extent
#
# ### Semantic errors
# - program runs fine but gives wrong answer
# - can be identified and removed by doing plenty of testing
# ## 1.8 The First Program
# - python programs are usually called scripts
# In[2]:
#----------------------------------------------------------
# hello world program
# by: John Doe
# Jan 1 2017
# Copyright: Anyone may freely copy or modify this program
#----------------------------------------------------------
print('hello world!') # say hello to the beautiful world!
# ## 1.9 Exercises
#
# ### 1. Write a hello world script
# - write a python script that prints "Hello World!" as an output on the console
#
# ### 2. Solve kattis hello problem
# - create an account in Kattis: https://open.kattis.com/login
# - login and solve the hello problem: https://open.kattis.com/problems/hello
#
# ### 3. ASCII Art
# - learn about ASCII Art
# - print some ASCII Arts, texts and pictures of your choice
# - use ASCII Art generator: http://patorjk.com/software/taag/#p=display&f=Graffiti&t=Type%20Something%20
#
# ### 4. Write a script that prints various stages of hangman game
# - game description: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hangman_(game)
# - produce the output seen in Example game section of the Wikipedia page
#
# In[ ]:
#
# ### input
# - get data from keyboard, a file, or some device
#
# ### output
# - display data/answer on screen, or save it to file or to a device
#
# ### math
# - basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
#
# ### conditional execution
# - check for certain condititions and execute appropriate sequence of statements
#
# ### repitition
# - perform some action repeatedly, usually with some variation every time
# ## 1.6 Debugging
# - finding and getting rid of bugs/errors
# - as long as humans write computer codes, there'll be always errors in computer program
# - although frustrating at times, it is one of the most intellectually rich, challenging, and interesting part of programming
# ## 1.7 Coding Errors
# - errors are also called bugs
# - 3 types: syntax, run-time and semantic
#
# ### Syntax errors
# - program needs to follow Python syntax or grammar; otherwise Python interpreter will not understand and tell programmers about the errors
# ### Run-time errors
# - also called run-time exceptions
# - errors appear while programming is running
# - can be handled to certain extent
#
# ### Semantic errors
# - program runs fine but gives wrong answer
# - can be identified and removed by doing plenty of testing
# ## 1.8 The First Program
# - python programs are usually called scripts
# In[2]:
#----------------------------------------------------------
# hello world program
# by: John Doe
# Jan 1 2017
# Copyright: Anyone may freely copy or modify this program
#----------------------------------------------------------
print('hello world!') # say hello to the beautiful world!
# ## 1.9 Exercises
#
# ### 1. Write a hello world script
# - write a python script that prints "Hello World!" as an output on the console
#
# ### 2. Solve kattis hello problem
# - create an account in Kattis: https://open.kattis.com/login
# - login and solve the hello problem: https://open.kattis.com/problems/hello
#
# ### 3. ASCII Art
# - learn about ASCII Art
# - print some ASCII Arts, texts and pictures of your choice
# - use ASCII Art generator: http://patorjk.com/software/taag/#p=display&f=Graffiti&t=Type%20Something%20
#
# ### 4. Write a script that prints various stages of hangman game
# - game description: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hangman_(game)
# - produce the output seen in Example game section of the Wikipedia page
#
# In[ ]: