#
# You can find the original Examples:
# https://opensees.berkeley.edu/wiki/index.php/Examples_Manual
# Original Examples by By Silvia Mazzoni & Frank McKenna, 2006, in Tcl
# Converted to OpenSeesPy by SilviaMazzoni, 2020
#
# #
# # Introductory Examples # The objective of Example 1a and Example 1b is to give an overview of input-file format in OpenSees using simple scripts. # These scripts do not take advantage of the Tcl scripting capabilities shown in the later examples. However, they do provide starting a place where the input file is similar to that of more familiar Finite-Element Analysis software. Subsequent examples should be used as the basis for user input files. # #
 #
# In[1]:
############################################################
# EXAMPLE:
# pyEx1b.Portal2D.Push.tcl.py
# for OpenSeesPy
# --------------------------------------------------------#
# by: Silvia Mazzoni, 2020
# silviamazzoni@yahoo.com
############################################################
# configure Python workspace
import openseespy.opensees as ops
import eSEESminiPy
import os
import math
import numpy as numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ops.wipe()
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example 1. portal frame in 2D
# static pushover analysis of Portal Frame, with gravity.
# all units are in kip, inch, second
# elasticBeamColumn ELEMENT
# Silvia Mazzoni and Frank McKenna, 2006
#
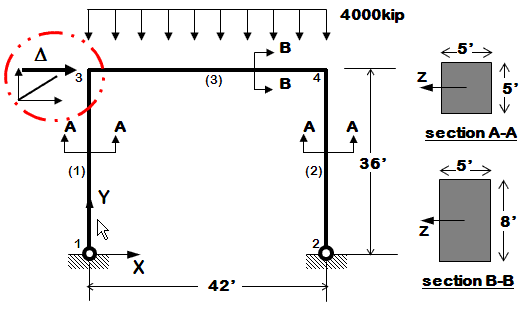
# ^Y
# or
# 3_________(3)________4 __
# or | |
# or | |
# or | |
# (1) (2) LCol
# or | |
# or | |
# or | |
# =1= =2= _or_ -------->X
# or----------LBeam------------|
#
# SET UP ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ops.wipe() # clear opensees model
ops.model('basic','-ndm',2,'-ndf',3) # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
if not os.path.exists('Data'):
os.mkdir('Data')
# define GEOMETRY -------------------------------------------------------------
# nodal coordinates:
ops.node(1,0,0) # node , X Y
ops.node(2,504,0)
ops.node(3,0,432)
ops.node(4,504,432)
# Single point constraints -- Boundary Conditions
ops.fix(1,1,1,1) # node DX DY RZ
ops.fix(2,1,1,1) # node DX DY RZ
ops.fix(3,0,0,0)
ops.fix(4,0,0,0)
# nodal masses:
ops.mass(3,5.18,0.,0.) # node , Mx My Mz, Mass=Weight/g.
ops.mass(4,5.18,0.,0.)
# Define ELEMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------
# define geometric transformation: performs a linear geometric transformation of beam stiffness and resisting force from the basic system to the global-coordinate system
ops.geomTransf('Linear',1) # associate a tag to transformation
# connectivity: (make A very large, 10e6 times its actual value)
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',1,1,3,3600000000,4227,1080000,1) # element elasticBeamColumn eleTag iNode jNode A E Iz transfTag
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',2,2,4,3600000000,4227,1080000,1)
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',3,3,4,5760000000,4227,4423680,1)
# Define RECORDERS -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.recorder('Node','-file','Data/DFreeEx1bPush.out','-time','-node',3,4,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of free nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file','Data/DBaseEx1bPush.out','-time','-node',1,2,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of support nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file','Data/RBaseEx1bPush.out','-time','-node',1,2,'-dof',1,2,3,'reaction') # support reaction
ops.recorder('Element','-file','Data/FColEx1bPush.out','-time','-ele',1,2,'globalForce') # element forces -- column
ops.recorder('Element','-file','Data/FBeamEx1bPush.out','-time','-ele',3,'globalForce') # element forces -- beam
# define GRAVITY -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',1) # timeSeries Linear 1;
# define Load Pattern
ops.pattern('Plain',1,1) #
ops.eleLoad('-ele',3,'-type','-beamUniform',-7.94) # distributed superstructure-weight on beam
ops.wipeAnalysis() # adding this to clear Analysis module
ops.constraints('Plain') # how it handles boundary conditions
ops.numberer('Plain') # renumber dofs to minimize band-width (optimization), if you want to
ops.system('BandGeneral') # how to store and solve the system of equations in the analysis
ops.test('NormDispIncr',1.0e-8,6) # determine if convergence has been achieved at the end of an iteration step
ops.algorithm('Newton') # use Newtons solution algorithm: updates tangent stiffness at every iteration
ops.integrator('LoadControl',0.1) # determine the next time step for an analysis, apply gravity in 10 steps
ops.analysis('Static') # define type of analysis static or transient
ops.analyze(10) # perform gravity analysis
ops.loadConst('-time',0.0) # hold gravity constant and restart time
# define LATERAL load -------------------------------------------------------------
# Lateral load pattern
ops.timeSeries('Linear',2) # timeSeries Linear 2;
# define Load Pattern
ops.pattern('Plain',2,2) #
ops.load(3,2000.,0.0,0.0) # node , FX FY MZ -- representative lateral load at top nodes
ops.load(4,2000.,0.0,0.0) # place 1/2 of the weight for each node to get shear coefficient
# pushover: diplacement controlled static analysis
ops.integrator('DisplacementControl',3,1,0.1) # switch to displacement control, for node 11, dof 1, 0.1 increment
ops.analyze(100) # apply 100 steps of pushover analysis to a displacement of 10
print('Done!')
# In[2]:
eSEESminiPy.drawModel()
# In[3]:
# plot deformed shape at end of analysis (it may have returned to rest)
# amplify the deformtions by 5
eSEESminiPy.drawDeformedShape(5)
# In[4]:
ops.wipe() # the wipe command here closes all recorder files
plt.close('all')
fname3 = 'Data/DFreeEx1bPush.out'
dataDFree = numpy.loadtxt(fname3)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.title('Ex1b.Portal2D.Push.tcl')
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot(dataDFree[:,1])
plt.xlabel('Step Number')
plt.ylabel('Free-Node Displacement')
plt.subplot(212)
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot(dataDFree[:,1],dataDFree[:,0])
plt.xlabel('Free-Node Disp.')
plt.ylabel('Pseudo-Time (~Force)')
print('End of Run: pyEx1b.Portal2D.Push.tcl.py')
#
# In[1]:
############################################################
# EXAMPLE:
# pyEx1b.Portal2D.Push.tcl.py
# for OpenSeesPy
# --------------------------------------------------------#
# by: Silvia Mazzoni, 2020
# silviamazzoni@yahoo.com
############################################################
# configure Python workspace
import openseespy.opensees as ops
import eSEESminiPy
import os
import math
import numpy as numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ops.wipe()
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example 1. portal frame in 2D
# static pushover analysis of Portal Frame, with gravity.
# all units are in kip, inch, second
# elasticBeamColumn ELEMENT
# Silvia Mazzoni and Frank McKenna, 2006
#
# ^Y
# or
# 3_________(3)________4 __
# or | |
# or | |
# or | |
# (1) (2) LCol
# or | |
# or | |
# or | |
# =1= =2= _or_ -------->X
# or----------LBeam------------|
#
# SET UP ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ops.wipe() # clear opensees model
ops.model('basic','-ndm',2,'-ndf',3) # 2 dimensions, 3 dof per node
if not os.path.exists('Data'):
os.mkdir('Data')
# define GEOMETRY -------------------------------------------------------------
# nodal coordinates:
ops.node(1,0,0) # node , X Y
ops.node(2,504,0)
ops.node(3,0,432)
ops.node(4,504,432)
# Single point constraints -- Boundary Conditions
ops.fix(1,1,1,1) # node DX DY RZ
ops.fix(2,1,1,1) # node DX DY RZ
ops.fix(3,0,0,0)
ops.fix(4,0,0,0)
# nodal masses:
ops.mass(3,5.18,0.,0.) # node , Mx My Mz, Mass=Weight/g.
ops.mass(4,5.18,0.,0.)
# Define ELEMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------
# define geometric transformation: performs a linear geometric transformation of beam stiffness and resisting force from the basic system to the global-coordinate system
ops.geomTransf('Linear',1) # associate a tag to transformation
# connectivity: (make A very large, 10e6 times its actual value)
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',1,1,3,3600000000,4227,1080000,1) # element elasticBeamColumn eleTag iNode jNode A E Iz transfTag
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',2,2,4,3600000000,4227,1080000,1)
ops.element('elasticBeamColumn',3,3,4,5760000000,4227,4423680,1)
# Define RECORDERS -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.recorder('Node','-file','Data/DFreeEx1bPush.out','-time','-node',3,4,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of free nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file','Data/DBaseEx1bPush.out','-time','-node',1,2,'-dof',1,2,3,'disp') # displacements of support nodes
ops.recorder('Node','-file','Data/RBaseEx1bPush.out','-time','-node',1,2,'-dof',1,2,3,'reaction') # support reaction
ops.recorder('Element','-file','Data/FColEx1bPush.out','-time','-ele',1,2,'globalForce') # element forces -- column
ops.recorder('Element','-file','Data/FBeamEx1bPush.out','-time','-ele',3,'globalForce') # element forces -- beam
# define GRAVITY -------------------------------------------------------------
ops.timeSeries('Linear',1) # timeSeries Linear 1;
# define Load Pattern
ops.pattern('Plain',1,1) #
ops.eleLoad('-ele',3,'-type','-beamUniform',-7.94) # distributed superstructure-weight on beam
ops.wipeAnalysis() # adding this to clear Analysis module
ops.constraints('Plain') # how it handles boundary conditions
ops.numberer('Plain') # renumber dofs to minimize band-width (optimization), if you want to
ops.system('BandGeneral') # how to store and solve the system of equations in the analysis
ops.test('NormDispIncr',1.0e-8,6) # determine if convergence has been achieved at the end of an iteration step
ops.algorithm('Newton') # use Newtons solution algorithm: updates tangent stiffness at every iteration
ops.integrator('LoadControl',0.1) # determine the next time step for an analysis, apply gravity in 10 steps
ops.analysis('Static') # define type of analysis static or transient
ops.analyze(10) # perform gravity analysis
ops.loadConst('-time',0.0) # hold gravity constant and restart time
# define LATERAL load -------------------------------------------------------------
# Lateral load pattern
ops.timeSeries('Linear',2) # timeSeries Linear 2;
# define Load Pattern
ops.pattern('Plain',2,2) #
ops.load(3,2000.,0.0,0.0) # node , FX FY MZ -- representative lateral load at top nodes
ops.load(4,2000.,0.0,0.0) # place 1/2 of the weight for each node to get shear coefficient
# pushover: diplacement controlled static analysis
ops.integrator('DisplacementControl',3,1,0.1) # switch to displacement control, for node 11, dof 1, 0.1 increment
ops.analyze(100) # apply 100 steps of pushover analysis to a displacement of 10
print('Done!')
# In[2]:
eSEESminiPy.drawModel()
# In[3]:
# plot deformed shape at end of analysis (it may have returned to rest)
# amplify the deformtions by 5
eSEESminiPy.drawDeformedShape(5)
# In[4]:
ops.wipe() # the wipe command here closes all recorder files
plt.close('all')
fname3 = 'Data/DFreeEx1bPush.out'
dataDFree = numpy.loadtxt(fname3)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.title('Ex1b.Portal2D.Push.tcl')
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot(dataDFree[:,1])
plt.xlabel('Step Number')
plt.ylabel('Free-Node Displacement')
plt.subplot(212)
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot(dataDFree[:,1],dataDFree[:,0])
plt.xlabel('Free-Node Disp.')
plt.ylabel('Pseudo-Time (~Force)')
print('End of Run: pyEx1b.Portal2D.Push.tcl.py')