
From Maps to Models - Tutorials for structural geological modeling using GemPy and GemGIS ¶
Example 1 - Folded Layers¶
This example will show how to convert the geological map below using GemGIS to a GemPy model. This example is based on digitized data. The area is 3942 m wide (W-E extent) and 2710 m high (N-S extent). The vertical extent varies between -200 m and 1000 m. The model represents two folded layers (purple and blue) above a basement (yellow).
- How to build your fourth GemPy model with input data generated through GemGIS
- How to build a GemPy model with folded layers
- How to obtain the the fold axis of a structure
- How to extract contour lines from a PyVista depth map and to save them as GeoDataFrame
- How to convert a depth map to an array/raster
- How to convert contour lines from that raster
Your Tasks¶
- Georeference the map in QGIS given the dimensions above using the coordinate reference system with the EPSG code 4326
- Digitize the layer boundaries (including a
formationcolumn) and the topographic lines (including aZcolumn) - Digitize so-called strike lines for the different layers. The orientations used for
GemPywill be calculated from the strike lines.
Contents¶
- Installing GemPy and GemGIS
- Importing Libraries
- Data Preparation
- GemPy Model calculation
- Model Visualization and Post-Processing
 Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 22, figure 9, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 22, figure 9, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Installing GemPy and GemGIS¶
If you have not installed GemPy yet, please follow the GemPy installation instructions and the GemGIS installation instructions. If you encounter any issues, feel free to open a new discussion at GemPy Discussions or GemGIS Discussions. If you encounter an error in the installation process, feel free to also open an issue at GemPy Issues or GemGIS Issues. There, the GemPy and GemGIS development teams will help you out.
Importing Libraries¶
For this notebook, we need the geopandas library for the data preparation, rasterio for dealing with the created digital elevation model, matplotlib for plotting, numpy for some numerical calculations, pandas for manipulating DataFrames and of course the gempy and gemgis libraries. Any warnings that may appear can be ignored for now. The file path is set to load the data provided for this tutorial.
import geopandas as gpd
import rasterio
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import gemgis as gg
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import gempy as gp
import pyvista as pv
import pandas as pd
file_path = '../../data/example05_folded_layers/'
Data Preparation¶
At his point, you should have the topographic contour lines (including a Z column) and the layer boundaries (including a formation column) digitized. If not, please generate the data before continuing with this tutorial.
Creating Digital Elevation Model from Contour Lines¶
The digital elevation model (DEM) will be created by interpolating the contour lines digitized from the georeferenced map using the SciPy Radial Basis Function interpolation wrapped in GemGIS. The respective function used for that is gg.vector.interpolate_raster().
There is also a tutorial available for this task on the GemGIS Documentation page.
 Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 22, figure 9, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 22, figure 9, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Loading contour lines¶
First, the contour lines are loaded using GeoPandas. Please provide here the name of your shape file containing the digitized topographic contour lines.
topo = gpd.read_file(file_path + 'topo5.shp')
topo.head()
Plotting the contour lines¶
The contour lines are plotted using the built-in plotting function of GeoPandas.
topo.plot(column='Z', aspect=1, legend=True, cmap='gist_earth')
Interpolating the contour lines¶
The digital elevation model (DEM) will be created by interpolating the contour lines digitized from the georeferenced map using the SciPy Radial Basis Function interpolation wrapped in GemGIS. The respective function used for that is gg.vector.interpolate_raster().
topo_raster = gg.vector.interpolate_raster(gdf=topo, value='Z', method='rbf', res=10)
Plotting the raster¶
The interpolated digital elevation model can be displayed using matplotlib and its plt.imshow() function and by providing the extent of the raster to align it with the contour lines.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
fix, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(10, 10))
topo.plot(ax=ax, aspect='equal', column='Z', cmap='gist_earth')
im = plt.imshow(topo_raster, origin='lower', extent=[0, 3942, 0, 2710], cmap='gist_earth')
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
cax = divider.append_axes("right", size="5%", pad=0.05)
cbar = plt.colorbar(im, cax=cax)
cbar.set_label('Altitude [m]')
ax.set_xlabel('X [m]')
ax.set_ylabel('Y [m]')
ax.set_xlim(0, 3942)
ax.set_ylim(0, 2710)
Saving the raster to disc¶
After the interpolation of the contour lines, the raster is saved to disc using gg.raster.save_as_tiff(). The function will not be executed as a raster is already provided with the example data.
topo_raster = rasterio.open(file_path + 'raster5.tif')
Processing Stratigraphic Boundaries¶
The interface points will be extracted from LineStrings digitized from the georeferenced map using QGIS. It is important to provide a formation name for each layer boundary. Up until now, only the X and Y position are stored in the vertices of the LineStrings. Using the digital elevation model created already, we will now sample the elevation model at the locations of the vertices to extract the height at this point as the stratigraphic boundary was mapped at the surface.
 Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 22, figure 9, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 22, figure 9, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
interfaces = gpd.read_file(file_path + 'interfaces5.shp')
interfaces.head()
Plotting Stratigraphic Boundaries¶
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(5,5))
interfaces.plot(ax=ax, column='formation', legend=True, aspect='equal')
plt.grid()
ax.set_xlabel('X [m]')
ax.set_ylabel('Y [m]')
Extracting Z coordinates from Digital Elevation Model¶
The vertical position of the interface point will be extracted from the digital elevation model using the GemGIS function gg.vector.extract_xyz(). The resulting GeoDataFrame now contains single points including the information about the respective formation as well as the X, Y, and Z location. This is all we need as preparational steps to generate input data for GemPy.
There is also a tutorial available for this task on the GemGIS Documentation page.
interfaces_coords = gg.vector.extract_xyz(gdf=interfaces, dem=topo_raster)
interfaces_coords = interfaces_coords.sort_values(by='formation', ascending=False)
interfaces_coords
Plotting the Interface Points¶
The interface points incuding their altitude (Z-) values and the digitized LineString can be plotted using matplotlib.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(10, 10))
interfaces.plot(ax=ax, column='formation', legend=True, aspect='equal')
interfaces_coords.plot(ax=ax, column='formation', legend=True, aspect='equal')
plt.grid()
ax.set_xlabel('X [m]')
ax.set_ylabel('Y [m]')
ax.set_xlim(0, 3942)
ax.set_ylim(0, 2710)
Processing Orientations¶
For this example, orientations must be calculated yourself. They will be calculated using functions implemented in GemGIS and the previously digitized strike lines.
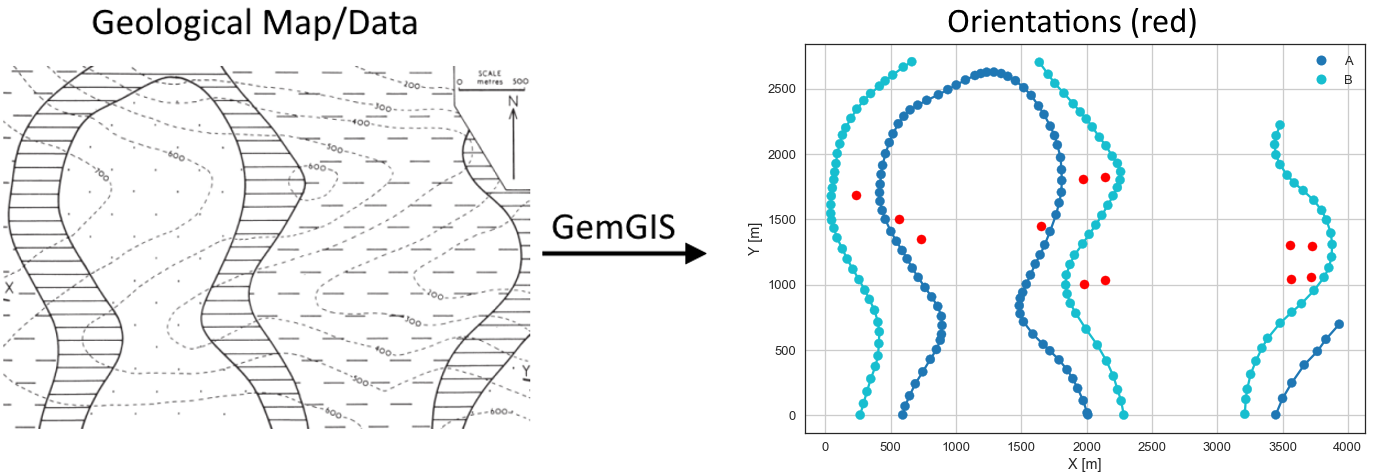 Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 22, figure 9, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 22, figure 9, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Orientations from Strike Lines¶
Strike lines connect outcropping stratigraphic boundaries (interfaces) of the same altitude. In other words: the intersections between topographic contours and stratigraphic boundaries at the surface. The height difference and the horizontal difference between two digitized lines is used to calculate the dip and azimuth and hence an orientation that is necessary for GemPy.
The calculation of orientations from strike lines has been implemented into GemPy for simple cases like these. In order to calculate the orientations, each set of strikes lines/LineStrings for one formation must be given an id number next to the altitude of the strike line. The id field is already predefined in QGIS. The strike line with the lowest altitude gets the id number 1, the strike line with the highest altitude the the number according to the number of digitized strike lines. It is currently recommended to use one set of strike lines for each structural element of one formation as illustrated.
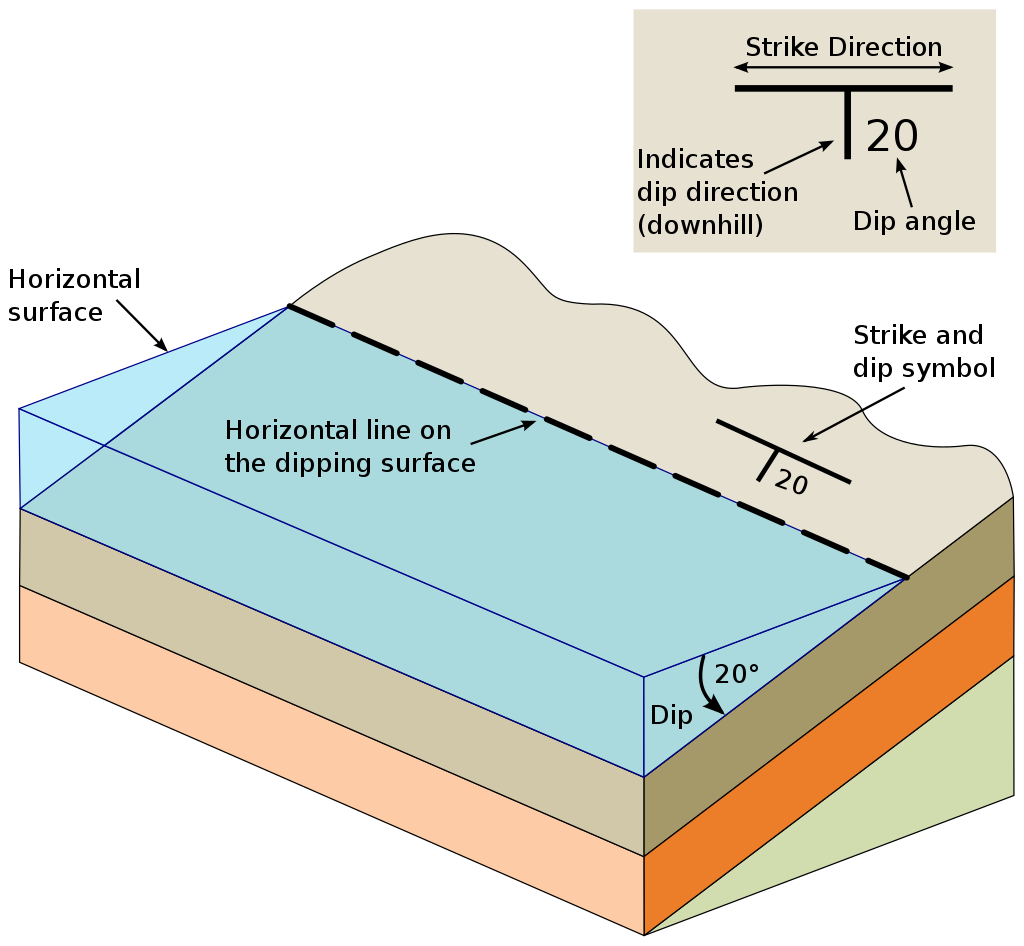
By CrunchyRocks, after Karla Panchuck - https://openpress.usask.ca/physicalgeology/chapter/13-5-measuring-geological-structures/, CC BY 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=113554289
 Source: Powell, D. (1995): Interpretation geologischer Strukturen durch Karten - Eine praktische Anleitung mit Aufgaben und Lösungen, page 14, figure 8, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-3-540-58607-4.
Source: Powell, D. (1995): Interpretation geologischer Strukturen durch Karten - Eine praktische Anleitung mit Aufgaben und Lösungen, page 14, figure 8, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-3-540-58607-4.
strikes = gpd.read_file(file_path + 'strikes5.shp')
strikes
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(5,5))
strikes.plot(ax=ax,column='id', aspect=1)
interfaces.plot(ax=ax, column='formation', legend=True, aspect='equal')
ax.set_xlabel('X [m]')
ax.set_ylabel('Y [m]')
ax.grid()
Calculate Orientations for each formation¶
The calculations will be calculated using the function gg.vector.calculate_orientations_from_strike_lines() where the strike lines for each single formation will be provided and calculated separately. The result is a GeoDataFrame ready to be used in GemPy.
orientations_a = gg.vector.calculate_orientations_from_strike_lines(gdf=strikes[strikes['formation'] == 'A'].sort_values(by='Z', ascending=True).reset_index())
orientations_a
orientations_a1 = gg.vector.calculate_orientations_from_strike_lines(gdf=strikes[strikes['formation'] == 'A1'].sort_values(by='Z', ascending=True).reset_index())
orientations_a1
orientations_a2 = gg.vector.calculate_orientations_from_strike_lines(gdf=strikes[strikes['formation'] == 'A2'].sort_values(by='Z', ascending=True).reset_index())
orientations_a2
orientations_b1 = gg.vector.calculate_orientations_from_strike_lines(gdf=strikes[strikes['formation'] == 'B1'].sort_values(by='Z', ascending=True).reset_index())
orientations_b1
orientations_b2 = gg.vector.calculate_orientations_from_strike_lines(gdf=strikes[strikes['formation'] == 'B2'].sort_values(by='Z', ascending=True).reset_index())
orientations_b2
orientations_b3 = gg.vector.calculate_orientations_from_strike_lines(gdf=strikes[strikes['formation'] == 'B3'].sort_values(by='Z', ascending=True).reset_index())
orientations_b3
orientations_b4 = gg.vector.calculate_orientations_from_strike_lines(gdf=strikes[strikes['formation'] == 'B4'].sort_values(by='Z', ascending=True).reset_index())
orientations_b4
Merging Orientations for GemPy¶
Since GemPy only takes one DataFrame for the necessary orientations, the single DataFrames are concatenated using pd.concat().
import pandas as pd
orientations = pd.concat([orientations_a, orientations_a1, orientations_a2, orientations_b1, orientations_b2, orientations_b3, orientations_b4]).reset_index()
orientations['formation'] = ['A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B']
orientations
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(10, 10))
interfaces.plot(ax=ax, column='formation', legend=True, aspect='equal')
interfaces_coords.plot(ax=ax, column='formation', legend=True, aspect='equal')
orientations.plot(ax=ax, color='red', aspect='equal')
plt.grid()
ax.set_xlabel('X [m]')
ax.set_ylabel('Y [m]')
ax.set_xlim(0, 3942)
ax.set_ylim(0, 2710)
GemPy Model Calculation¶
The creation of a GemPy Model follows particular steps which will be performed in the following:
- Create new model:
gp.create_model() - Data Initiation:
gp.init_data() - Map Stack to Surfaces:
gp.map_stack_to_surfaces() - [...]
- Set the Interpolator:
gp.set_interpolator() - Computing the Model:
gp.compute_model()
Creating the GemPy Model¶
The first step is to create a new empty GemPy model by providing a name for it.
geo_model = gp.create_model('Model5')
geo_model
Data Initiation¶
During this step, the extent of the model (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax, zmin, zmax) and the resolution in X, Yand Z direction (res_x, res_y, res_z, equal to the number of cells in each direction) will be set using lists of values.
The interface points (surface_points_df) and orientations (orientations_df) will be passed as pandas DataFrames.
gp.init_data(geo_model, [0, 3942, 0, 2710, -200, 1000], [100, 100, 100],
surface_points_df=interfaces_coords[interfaces_coords['Z'] != 0],
orientations_df=orientations,
default_values=True)
Inspecting the Surfaces¶
The model consists of two different layers or surfaces now which all belong to the Default series. During the next step, the proper Series will be assigned to the surfaces. Using the surfaces-attribute again, we can check which layers were loaded.
geo_model.surfaces
Inspecting the Input Data¶
The loaded interface points and orientations can again be inspected using the surface_points- and orientations-attributes. Using the df-attribute of this object will convert the displayed table in a pandas DataFrame.
geo_model.surface_points.df.head()
geo_model.orientations.df.head()
Map Stack to Surfaces¶
During this step, all two layers of the model are assigned to the Strata1 series. We know that the layers modeled here are parallel. If the layers were not parallel as shown in the next models, multiple series would be defined. We will also add a Basement here (geo_model.add_surfaces('Basement')). The order within one series also defines the age relations within this series and has to be according to the depositional events of the layers.
gp.map_stack_to_surfaces(geo_model,
{
'Strata1': ('A', 'B'),
},
remove_unused_series=True)
geo_model.add_surfaces('Basement')
Showing the Number of Data Points¶
You can also return the number of interfaces and orientations for each formation using gg.utils.show_number_of_data_points()
gg.utils.show_number_of_data_points(geo_model=geo_model)
Loading Digital Elevation Model¶
GemPy is capable of including a topography into the modeling process. Here, we use the topography that we have interpolated in one of the previous steps. GemPy takes the file path of the raster/digital elevation model and loads it as grid into the geo_model object.
geo_model.set_topography(
source='gdal', filepath=file_path + 'raster5.tif')
Defining Custom Section¶
It is possible to define straight (no bending) custom sections in GemPy that will be calculated additionally with a provided resolution and that can be displayed separately using matplotlib.
For this example, the X and Y indicate the location of the custom section. This custom section can be digitized with a LineString (line shape file) with vertices at both ends and loaded using GeoPandas.
The function gg.utils.to_section_dict() converts the GeoDataFrame into a custom section dict before it can be set as section grid for the geo_model object and plotted using the built-in plotting function.
custom_section = gpd.read_file(file_path + 'customsection5.shp')
custom_section_dict = gg.utils.to_section_dict(custom_section, section_column='name')
geo_model.set_section_grid(custom_section_dict)
gp.plot.plot_section_traces(geo_model)
Plotting the input data in 2D using Matplotlib¶
The input data can now be visualized in 2D using matplotlib. This might for example be useful to check if all points and measurements are defined the way we want them to. Using the function plot_2d(), we attain a 2D projection of our data points onto a plane of chosen direction (we can choose this attribute to be either 'x', 'y', or 'z').
gp.plot_2d(geo_model, direction='z', show_lith=False, show_boundaries=False)
plt.grid()
Plotting the input data in 3D using PyVista¶
The input data can also be viszualized using the pyvista package. In this view, the interface points are visible as well as the orientations (marked as arrows) which indicate the normals of each orientation value.
gp.plot_3d(geo_model, image=False, plotter_type='basic', notebook=True)
Setting the interpolator¶
Once we have made sure that we have defined all our primary information, we can continue with the next step towards creating our geological model: preparing the input data for interpolation.
Setting the interpolator is necessary before computing the actual model. Here, the most important kriging parameters can be defined.
gp.set_interpolator(geo_model,
compile_theano=True,
theano_optimizer='fast_compile',
verbose=[],
update_kriging=False
)
Computing the model¶
At this point, we have all we need to compute our full model via gp.compute_model(). By default, this will return two separate solutions in the form of arrays. The first provides information on the lithological formations, the second on the fault network in the model, which is not present in this example.
sol = gp.compute_model(geo_model, compute_mesh=True)
sol
geo_model.solutions
Model Visualization and Post-Processing¶
Visulazing Cross Sections of the computed model¶
Cross sections in different directions and at different cell_numbers can be displayed. Here, we see the layers of the model in the different directions.
The first section to be plotted is the custom section Section1 followed by an array of cross sections.
gp.plot_2d(geo_model, section_names=['Section1'], show_topography=True, show_data=False)
gp.plot_2d(geo_model, direction=['x', 'x', 'y', 'y'], cell_number=[25, 75, 25, 75], show_topography=True, show_data=False)
Next to the lithology data, we can also plot the calculated scalar field.
gp.plot_2d(geo_model, direction='y', show_data=False, show_scalar=True, show_lith=False)
Visualizing the computed model in 3D¶
The computed model can be visualized in 3D using the pyvista library. Setting notebook=False will open an interactive windows and the model can be rotated and zooming is possible.
gpv = gp.plot_3d(geo_model, image=False, show_topography=True,
plotter_type='basic', notebook=True, show_lith=True)
Post Processing¶
Now that the model has been created, we would like to utilize it. In this notebook, you will learn how to extract the fold axis of folded structures, how to extract contour lines from a PyVista depth map and how to save the contour lines as GeoDataFrame, how to convert a depth map to an array or raster, respectively. Lastly, you will learn how to extract the contour lines from raster.
Extracting the fold axis¶
The fold axis is the line along which the dip of the layers equals 0. Due to the shape of the mesh, a threshold value of 5° degrees is chosen to illustrate the location of the fold axis. First, we are exporting the depth maps using gg.visualization.create_depth_maps_from_gempy().
dict_all = gg.visualization.create_depth_maps_from_gempy(geo_model=geo_model,
surfaces=['A', 'B'])
dict_all
import pyvista as pv
p = pv.Plotter(notebook=True)
p.add_mesh(dict_all['A'][0], scalars='Depth [m]')
p.add_mesh(dict_all['A'][0].contour(), color='white')
p.add_mesh(dict_all['B'][0], scalars='Depth [m]')
p.add_mesh(dict_all['B'][0].contour(), color='white')
p.set_background('white')
p.show_grid(color='black')
p.show()
Then, we are computing the normals and calculate the dips and azimuths of each normal. The normals are represented by the entries l, m, and n. The results will then be added to the mesh as Data Array.
mesh = dict_all['B'][0]
mesh.compute_normals(inplace=True)
# Calculating the dips
dips = [90 - np.rad2deg(-np.arcsin(mesh['Normals'][i][2])) * (-1) for i in
range(len(mesh['Normals']))]
# Calculating the azimuths
azimuths = [np.rad2deg(np.arctan(mesh['Normals'][i][0] / mesh['Normals'][i][1])) + 180 for i in
range(len(mesh['Normals']))]
# Assigning dips and azimuths to scalars
mesh['Dips [°]'] = dips
mesh['Azimuths [°]'] = azimuths
mesh
We will then filter the cells where the dip of the mesh is <5° and create a PolyData dataset from it. This dataset represents the location of the fold axis.
indices = np.where(mesh['Dips [°]']<5)
indices[0][:10]
cells = mesh.cell_centers().points[indices]
cells[:10]
polydata_cells = pv.PolyData(cells)
polydata_cells
import pyvista as pv
p = pv.Plotter(notebook=True)
p.add_mesh(mesh)
p.add_mesh(polydata_cells, color='red')
p.set_background('white')
p.show_grid(color='black')
p.show()
Extracting contour lines from PyVista Mesh¶
Sometimes, it is more practical to display contour lines instead of the depth map (as mesh). This section illustrates how to extract these from a PyVista mesh and how to save it as GeoDataFrame to export it as shape file. We will use gg.vector.create_linestrings_from_contours() to do that.
There is also a tutorial available for this task on the GemGIS Documentation page.
contours = dict_all['B'][0].contour(np.arange(-200, 1000, 50))
contours
import pyvista as pv
p = pv.Plotter(notebook=True)
p.add_mesh(dict_all['B'][0], scalars='Depth [m]')
p.add_mesh(contours, color='white')
p.set_background('white')
p.show_grid(color='black')
p.show()
We will use gg.vector.create_linestrings_from_contours() to extract the contour lines from the mesh. Therefore, the function takes the PolyData dataset representing the contour lines.
gdf_linestrings = gg.vector.create_linestrings_from_contours(contours=contours,
return_gdf=True,
crs='EPSG:4326')
gdf_linestrings
gdf_linestrings.plot(aspect=1, column='Z', cmap='viridis', legend=True)
Converting PyVista Mesh to Array¶
Instead of displaying the depth map as mesh, we can also display the depth map as array which in return can be exported as .tif-file for a visualization in QGIS.
There is also a tutorial available for this task on the GemGIS Documentation page.
z_values = gg.utils.extract_zmap_data(surface=mesh,
cell_width=10)
z_values
z_values[z_values == -9999] = np.nan
im = plt.imshow(z_values, cmap='viridis', extent=mesh.bounds[:4])
cbar = plt.colorbar(im)
cbar.set_label('Altitude [m]')
plt.grid()
gg.raster.save_as_tiff(raster=z_values,
path= file_path + 'output_raster.tif',
extent= list(mesh.bounds[:4]),
crs='EPSG:4326',
overwrite_file=True)
Extracting Contour Lines from Raster/Array¶
Contour lines cannot only be extracted from a PyVista Mesh but also from the converted raster using gg.raster.extract_contour_lines_from_raster(). The results can be compared with the results of gg.vector.create_linestrings_from_contours().
There is also a tutorial available for this task on the GemGIS Documentation page.
z_values
gdf_lines = gg.raster.extract_contour_lines_from_raster(raster= z_values,
extent=mesh.bounds[:4],
target_crs='EPSG:4326',
interval = 50)
gdf_lines.head()
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(14, 5))
gdf_linestrings.plot(ax=ax1, aspect=1, column='Z', cmap='viridis', legend=True)
ax1.set_xlabel('X [m]')
ax1.set_ylabel('Y [m]')
ax1.set_xlim(0, 3942)
ax1.set_ylim(0, 2710)
ax1.grid()
gdf_lines.plot(ax=ax2, aspect=1, column='Z', cmap='viridis', legend=True)
ax2.set_xlabel('X [m]')
ax2.set_ylabel('Y [m]')
ax2.set_xlim(0, 3942)
ax2.set_ylim(0, 2710)
ax2.grid()
Conclusions¶
- How to build your fourth GemPy model with input data generated through GemGIS
- How to build a GemPy model with folded layers
- How to obtain the the fold axis of a structure
- How to extract contour lines from a PyVista depth map and to save them as GeoDataFrame
- How to convert a depth map to an array/raster
- How to convert contour lines from that raster
Outlook¶
- How to build your fifth GemPy model with input data generated through GemGIS
- How to sample rasters (interfaces/orientations)
- How to calculate raster properties and how to perform raster operations
- How to visualize the input data in PyVista
Take me to the next notebook on Github
Take me to the next notebook locally
 Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 26, figure 11, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Source: Bennison, G.M. (1988): An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, page 26, figure 11, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ISBN: 978-1-4615-9632-5
Licensing¶
Institute for Computational Geoscience, Geothermics and Reservoir Geophysics, RWTH Aachen University & Fraunhofer IEG, Fraunhofer Research Institution for Energy Infrastructures and Geothermal Systems IEG, Authors: Alexander Juestel. For more information contact: alexander.juestel(at)ieg.fraunhofer.de
All notebooks are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). References for each displayed map are provided. Most of the maps originate from the books of Powell (1992) and Bennison (1990). References for maps with unknown origin will gladly be added.