Exploring Xarray-spatial Local Tools Functions¶
Local tools operate at the cell level, where values with the same position from a set of input rasters are used to calculate the values of the cells at the output raster. Some examples of the application of local tools are:
- Change over time: You can use local tools to identify places where a value like land use or temperature changed over time.
- Aggregate over time: You can use local tools to aggregate values over time, for example calculating the average rainfall or hours of sunshine for each cell.
- Threshold over time: You can use local tools to identify places where a value is above or below a specified threshold, for example where the temperature was below a 0 °C.
- Data aggregation: You can use local tools to calculate the cost surface of an area, summing up different types of cost over the same cell in different layers.
In this notebook, we'll demonstrate how to use the Xarray-spatial local tools functions supported by Numpy. The spatial functions available are:
Creating the sample data¶
In order to present the functions in a very simple and easy to understand way, we'll use 4x4 data arrays and create an xarray.Dataset.
import numpy as np
import xarray as xr
arr = xr.DataArray([[2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 2, 2]], name="arr")
arr1 = xr.DataArray(
[[np.nan, 4, 2, 0], [2, 3, np.nan, 1], [5, 1, 2, 0], [1, 3, 2, np.nan]], name="arr1"
)
arr2 = xr.DataArray(
[[3, 1, 1, 2], [4, 1, 2, 5], [0, 0, 0, 0], [np.nan, 1, 1, 1]], name="arr2"
)
arr3 = xr.DataArray(
[[3, 3, 2, 0], [4, 1, 3, 1], [6, 1, 2, 2], [0, 0, 1, 1]], name="arr3"
)
raster_ds = xr.merge([arr, arr1, arr2, arr3])
Helping function¶
This function will be used to plot the arrays for all the examples in this notebook.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_arrays(arr_list, title_list):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=len(arr_list), figsize=(15, 10))
for idx, arr in zip(range(0, len(arr_list)), arr_list):
for i in range(arr.shape[0]):
for j in range(arr.shape[1]):
ax[idx].text(
j,
i,
int(arr.data[i, j]) if str(arr.data[i, j]) != "nan" else np.nan,
ha="center",
va="center",
color="black",
)
ax[idx].imshow(arr.values, cmap="tab20c_r")
ax[idx].set_xticks([])
ax[idx].set_yticks([])
ax[idx].set_title(title_list[idx])
plt.show()
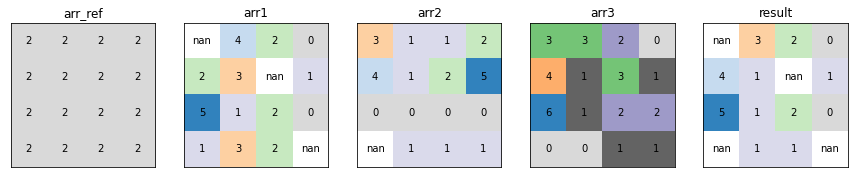
Cell Statistics¶
xrspatial.local.cell_stats calculates statistics from a raster dataset on a cell-by-cell basis.
from xrspatial.local import cell_stats
func_list = ["max", "mean", "median", "min", "std", "sum"]
statistics = [
cell_stats(raster=raster_ds[["arr1", "arr2", "arr3"]], func=func)
for func in func_list
]
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
raster_ds["arr3"],
],
["arr1", "arr2", "arr3"],
)
plot_arrays(statistics, func_list)
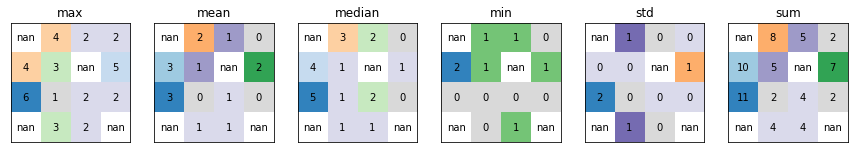

Combine¶
xrspatial.local.combine combines multiple arrays from a raster dataset, assigning a unique output value to each unique combination of raster values.
from xrspatial.local import combine
result_arr = combine(raster=raster_ds[["arr1", "arr2"]])
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
result_arr,
],
["arr1", "arr2", "result"],
)
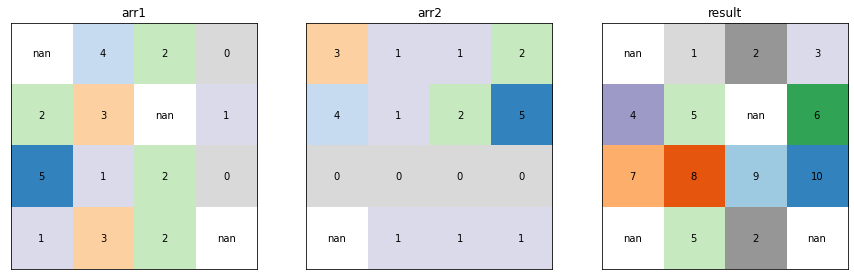
Lesser-Frequency¶
xrspatial.local.lesser_frequency calculates, given a raster dataset, the number of times the data variables values are lower than the values of a given reference data variable on a cell-by-cell basis.
from xrspatial.local import lesser_frequency
result_arr = lesser_frequency(raster=raster_ds, ref_var="arr")
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr"],
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
raster_ds["arr3"],
result_arr,
],
["arr_ref", "arr1", "arr2", "arr3", "result"],
)
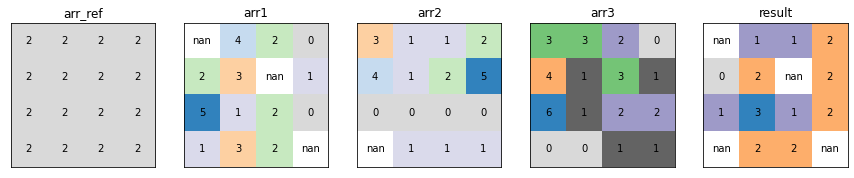
Equal Frequency¶
xrspatial.local.equal_frequency calculates, given a raster dataset, the number of times the data variables values are equal than the values of a given reference data variable on a cell-by-cell basis.
from xrspatial.local import equal_frequency
result_arr = equal_frequency(raster=raster_ds, ref_var="arr")
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr"],
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
raster_ds["arr3"],
result_arr,
],
["arr_ref", "arr1", "arr2", "arr3", "result"],
)
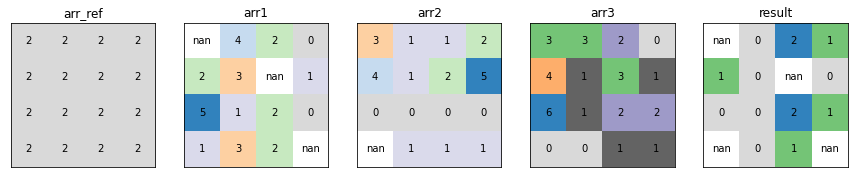
Greater Frequency¶
xrspatial.local.greater_frequency calculates, given a raster dataset, the number of times the data variables values are greater than the values of a given reference data variable on a cell-by-cell basis.
from xrspatial.local import greater_frequency
result_arr = greater_frequency(raster=raster_ds, ref_var="arr")
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr"],
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
raster_ds["arr3"],
result_arr,
],
["arr_ref", "arr1", "arr2", "arr3", "result"],
)
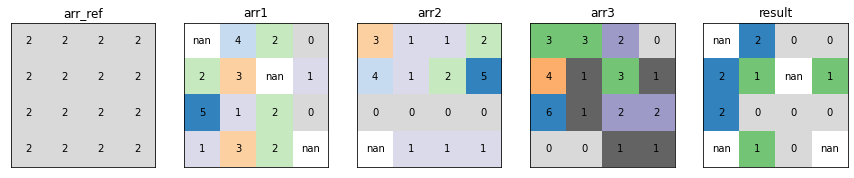
Lowest Position¶
xrspatial.local.lowest_position calculates the data variable index of the lowest value on a cell-by-cell basis.
from xrspatial.local import lowest_position
result_arr = lowest_position(raster=raster_ds)
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
raster_ds["arr3"],
result_arr,
],
["arr1", "arr2", "arr3", "result"],
)
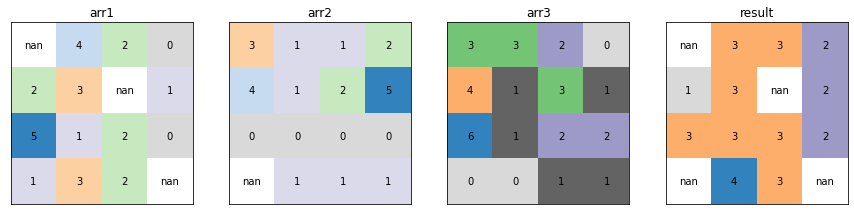
Highest Position¶
xrspatial.local.highest_position calculates the data variable index of the highest value on a cell-by-cell basis.
from xrspatial.local import highest_position
result_arr = highest_position(raster=raster_ds)
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
raster_ds["arr3"],
result_arr,
],
["arr1", "arr2", "arr3", "result"],
)
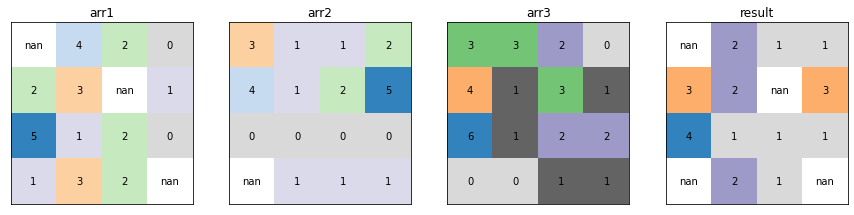
Popularity¶
xrspatial.local.popularity calculates the number of occurrences of each value of a raster dataset, on a cell-by-cell basis. The output value is assigned based on the reference data variable nth most popular.
from xrspatial.local import popularity
result_arr = popularity(raster=raster_ds, ref_var="arr")
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr"],
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
raster_ds["arr3"],
result_arr,
],
["arr_ref", "arr1", "arr2", "arr3", "result"],
)
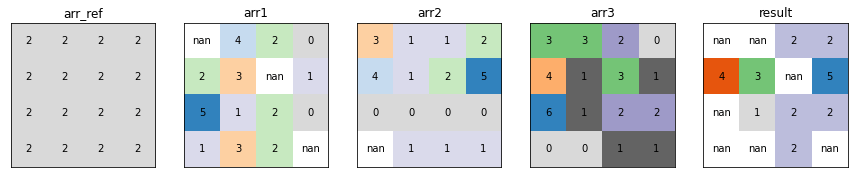
Rank¶
xrspatial.local.rank calculates the rank of each value of a raster dataset, on a cell-by-cell basis. The output value is assigned based on the rank of the reference data variable rank.
from xrspatial.local import rank
result_arr = rank(raster=raster_ds, ref_var="arr")
plot_arrays(
[
raster_ds["arr"],
raster_ds["arr1"],
raster_ds["arr2"],
raster_ds["arr3"],
result_arr,
],
["arr_ref", "arr1", "arr2", "arr3", "result"],
)