%pip install semantic-link-labs
Import the library¶
import sempy_labs as labs
from sempy_labs import lakehouse as lake
from sempy_labs import directlake
import sempy_labs.report as rep
dataset_name = ''
workspace_name = None
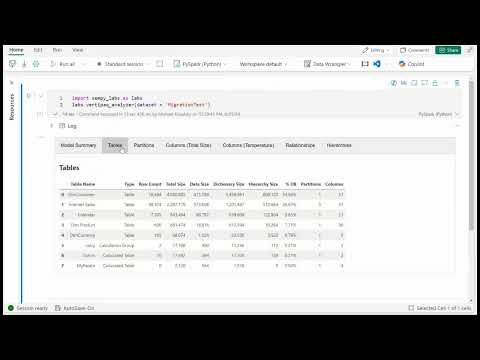
Vertipaq Analyzer¶
labs.vertipaq_analyzer(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name)
Export the Vertipaq Analyzer results to a .zip file in your lakehouse
labs.vertipaq_analyzer(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name, export='zip')
Export the Vertipaq Analyzer results to append to delta tables in your lakehouse.
labs.vertipaq_analyzer(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name, export='table')
Visualize the contents of an exported Vertipaq Analzyer .zip file.
labs.import_vertipaq_analyzer(folder_path='', file_name='')
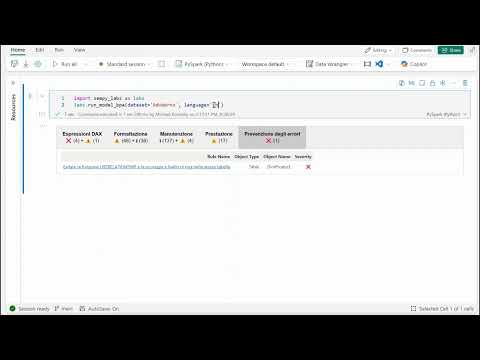
Best Practice Analzyer¶
This runs the standard rules for semantic models posted on Microsoft's GitHub.
labs.run_model_bpa(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name)
This runs the Best Practice Analyzer and exports the results to the 'modelbparesults' delta table in your Fabric lakehouse.
labs.run_model_bpa(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name, export=True)
This runs the Best Practice Analyzer with the rules translated into Italian (can enter any language in the 'language' parameter).
labs.run_model_bpa(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name, language='italian')
Run BPA using your own best practice rules¶
import sempy
sempy.fabric._client._utils._init_analysis_services()
import Microsoft.AnalysisServices.Tabular as TOM
import pandas as pd
dataset_name = ''
workspace_name = ''
rules = pd.DataFrame(
[
(
"Performance",
"Table",
"Warning",
"Rule name...",
lambda obj, tom: tom.is_calculated_table(table_name=obj.Name),
'Rule description...',
'',
),
(
"Performance",
"Column",
"Warning",
"Do not use floating point data types",
lambda obj, tom: obj.DataType == TOM.DataType.Double,
'The "Double" floating point data type should be avoided, as it can result in unpredictable roundoff errors and decreased performance in certain scenarios. Use "Int64" or "Decimal" where appropriate (but note that "Decimal" is limited to 4 digits after the decimal sign).',
)
],
columns=[
"Category",
"Scope",
"Severity",
"Rule Name",
"Expression",
"Description",
"URL",
],
)
labs.run_model_bpa(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name, rules=rules)
Translate a semantic model's metadata¶
labs.translate_semantic_model(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name, languages=['italian', 'japanese', 'hindi'], exclude_characters='_')
Direct Lake¶
Check if any lakehouse tables will hit the Direct Lake guardrails.
lake.get_lakehouse_tables(lakehouse=None, workspace=None, extended=True, count_rows=False)
lake.get_lakehouse_tables(lakehouse=None, workspace=None, extended=True, count_rows=False, export=True)
Check if any tables in a Direct Lake semantic model will fall back to DirectQuery.
directlake.check_fallback_reason(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name)
lake.optimize_lakehouse_tables(tables=['', ''], lakehouse=None, workspace=None)
Refresh/reframe your Direct Lake semantic model and restore the columns which were in memory prior to the refresh.
directlake.warm_direct_lake_cache_isresident(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name)
Ensure a warm cache for your users by putting the columns of a Direct Lake semantic model into memory based on the contents of a perspective.
Perspectives can be created either in Tabular Editor 3 or in Tabular Editor 2 using the Perspective Editor.
directlake.warm_direct_lake_cache_perspective(dataset=dataset_name, workspace=workspace_name, perspective='', add_dependencies=True)